SEXUAL REPRODUCTION
- gametes of two parents fuse to give rise to a zygote is called sexual reproduction.
- Male and female gametes are formed either by the same individual or different individual of the opposite sex.
- off springs that are not identical to the parents and to each other
- All the sexually reproductive organism have three phases in their life-
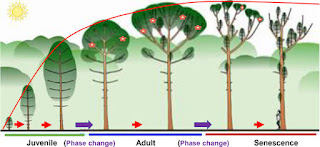
- Juvenile phase- the period of growth from birth to reproductive maturity in animals
- in plants this inter flowering period is known as vegetative phase.
- Reproductive phase- in this phase, the organisms reproduce sexually.
- Senescent phase- the phase between reproductive maturity and death of an organism, characterized by gradual deterioration in the body leading to the death of an organism.
Based on the life span of plants, plants can be differentiated into 3 types-
- Annual plants- live for one year and start flowering at the end of the year.
- Biennials plants- live for two years and start flowering in the second year.
- Perennial plants- live for several years --flower only once in their life time.
Example- bamboo species flower only once in 50-100 years.
Strobilanthuskunthiana flowers once in 12 years.
Most of the perennial plants flower each year.
- Many mammals reproduce only during favourable season in their reproductive phase and hence these organisms are called as seasonal breeders. Example- cow, buffalo.
- Some mammals actively reproduce throughout their reproductive phase and hence are called as continuous breeders. Example- man, rabbit.
- Some cyclic changes occur in the female reproductive system of female mammals which is called as reproductive cycle.
- Reproductive cycle is of two types –
- Menstrual cycle- the cycle of primates in which changes carry on all the year with one ovulation in a month is called menstrual cycle. Example- apes, humans.
- Oestrous cycle- the reproductive cycle in non-primate females
- It consists of a short period during which female receives the male for mating followed by the events of sexual reproduction Example- cow, tiger etc.
Events in sexual reproduction
- Events of sexual reproduction is grouped under three categories-
- Pre-fertilization events-
- The events of sexual reproduction which occurs before fertilization
- Pre- fertilization events are a) gametogenesis and b) gamete transfer.
- Fertilization events- The process of fusion of male and female gametes to form a zygote is called fertilization or syngamy.
Post- fertilization events-
- A diploid zygote is formed as a result of fertilization.
- The process of development of embryo from the zygote is called embryogenesis
PRE- FERTILIZATION
- The events of sexual reproduction which occurs before fertilization.
- Pre- fertilization events are a) gametogenesis and b) gamete transfer.
- Gametogenesis-
- The process of formation of gametes
- gametes are the specialized haploid cells and are of two types- male and female gametes.
- When both the gametes are similar in appearance that these can not be distinguished, these gametes are called homogametes or isogametes. Example- algae
- Gametes are haploid even though the parent body is diploid.
- If the parent is haploid, the parents produce gamete by mitosis. Example- monera, algae
- In diploid parents, the parents produce gametes by meiosis, the reduction division to produce haploid gametes. Example- human beings, higher plants.
- In diploid organisms, the gamete mother cells --meiosis -- gametes are called meiocytes - haploid.
- Human beings are diploid organisms and have 46 chromosomes and so the gametes contain 23, half of the number of chromosome by reduction division








No comments:
Post a Comment