BACTERIAL DISEASES
Typhoid
- Also known as- enteric fever.
- Pathogen- Salmonella typhi.
- Transmitted by contaminated food and water.
- Symptoms- Sustained high fever (39° to 40°C), weakness, stomach pain, constipation, headache and loss of appetite, intestinal perforation and death may occur in severe cases.
- Also migrates to other parts of the body.
- confirmed by Widal test. (Serological test)
- Treatment is done by antibiotics.
- typhoid carriers do not have the disease but still can spread the bacteria. Eg. Typhoid mary. (Cook)
- Prevention- use clean water(boiled), wash hands, avoid raw vegetables, clean fruits and vegetables.
Pneumonia
- Caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae. (Pneumococcus)
- Transmitted by droplets released by infected person, sharing glasses and utensils.
- Mainly affects lungs- alveoli.
- Common symptoms are fever, chills, cough and headache, difficulty in breathing and in severe cases lips and finger nails turn gray to bluish colour.
- Some types are preventable by vaccines.
Dysentry
- Caused by shigella.
- Mode of transmission- by contaminated food and water.
- Affects intestines.
- Symptoms- fever, diarrhoea abdominal cramps, nausea, vomiting.
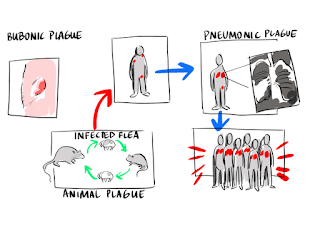
Plague
- Aka black death.
- Caused by Yersinia pestis
- Bacteria lives in rodents (rats, squirrels) and rat flea.
- Mode of transmissions- when flea bites human, they inject bacteria
- Several types, most common is - Bubonic plague
- Symptoms- enlarged lymph node, fever ,chills, muscle ache, fatigue.
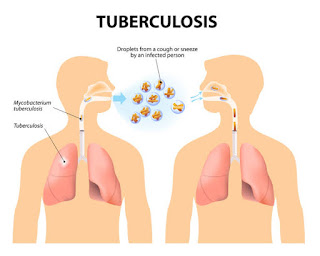
Tuberculosis





No comments:
Post a Comment