IMMUNE SYSTEM IN THE BODY
Immune system consists of-
- Lymphoid organs
- Lymphoid tissues
- B- cells and T-cells
- Antibodies
Lymphoid organs-
The organs where origin and/or maturation and proliferation of lymphocytes.
Lymphoid organs are of two types-
1. Primary lymphoid organs
2. Secondary lymphoid organs.
1. The primary lymphoid organs - bone marrow and thymus -- immature lymphocytes differentiate into antigen-sensitive lymphocytes.
The bone marrow is the main lymphoid organ where all blood cells including lymphocytes are produced.
The thymus is a lobed organ located near the heart and beneath the breastbone.
2. Secondary lymphoid organs- Spleen, tonsil, lymph node, Peyer’s patches of small intestine and appendix- proliferation of lymphocytes.
The secondary lymphoid organs -- interaction of lymphocytes with the antigen -- proliferate -- effector cells.
The spleen is a large bean shaped organ mainly contains lymphocytes and phagocytes - acts as a filter of the blood by trapping blood-borne microorganisms and has a large reservoir of erythrocytes.
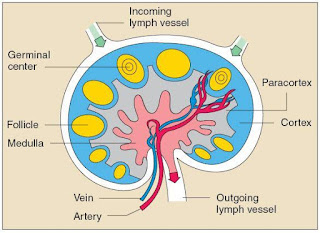
The lymph nodes are small solid structures located at different points along the lymphatic system.
Tonsils
Appendix
Peyer's patches
Lymphoid tissue-
Lymphoid tissue are located within the lining of the respiratory, digestive and urogenital tracts.
Lymphoid tissues are also called mucosalassociated lymphoid tissue (MALT) which constitutes about 50 per cent ofthe lymphoid tissue in human body.









No comments:
Post a Comment