CELL ORGANELLES - 2
PLASTIDS
- present in the plant cells
- bear some specific pigments -- specific colours to the plants.
- Based on the type of pigments plastids can be classified into chloroplasts, chromoplasts and leucoplasts.
- The chloroplasts contain chlorophyll and carotenoid pigments -- trap light energy essential for photosynthesis.
- In the chromoplasts, fat soluble carotenoid pigments like carotene, xanthophylls and others are present.
- The leucoplasts -- no pigments --colourless
- store nutrients 1. amyloplasts - store carbohydrates
- 2. elaioplasts store oils and fats, 3. aleuroplasts store proteins.
- Chloroplasts of the green plants are found in the mesophyll cells of the leaves.
- The chloroplasts are double membrane bound.
- The space limited by the inner membrane of the chloroplast -- stroma.
- A number of organised flattened membranous sacs -- thylakoids.
- Thylakoids are arranged in stacks like the piles of coins called grana.
- There are flat membranous tubules called the stroma lamellae connecting the thylakoids of the different grana.
- The membrane of the thylakoids enclose a space -- lumen.
- stroma -- enzymes, double stranded DNA molecules, ribosomes.
RIBOSOMES
- Ribosomes are the granular structures composed of ribonucleic acid (RNA) and proteins.
- The eukaryotic ribosomes are 80S
- ‘S’ stands for the sedimentation coefficient - indirectly is a measure of density and size.
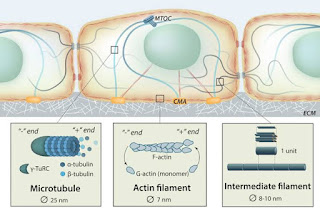
CYTOSKELETON
- An elaborate network of filamentous proteinaceous structures -- in the cytoplasm.
- Function- provides mechanical support, motility, and maintains the shape of the cell.










No comments:
Post a Comment