LINKAGE AND RECOMBINATION
- Morgan carried out several dihybrid crosses in Drosophila melanogaster to study genes that were sex-linked - discovered variation
- Why drosophila (fruitfly)--
- 1. Can be grown in simple medium
- 2. Male female easily distinguishable
- 3. Short life cycle
- 4. Produce large no of progeny
- 5. Various features can be seen with low power microscope.
- Morgan hybridized yellow-bodied, white-eyed females to brown-bodied, red-eyed males and intercrossed those F1
- According to him, two genes did not segregate independent of each other and F2 ratio deviated from 9:3:3:1.
- This concluded that genes are linked. When they are located on same chromosome. This process is called linkage.
- This forms more parental combinations.
- Some pair are tightly linked - very less recombination
- Some are loosely linked- show slight more recombination
- Recombination is the rearrangement of genetic material. The generation of non-parental gene combination during dihybrid cross is called recombination.
- When genes are located on same chromosome, they are tightly linked and show less linkage. This is responsible for variation.
Linkage depends on distance between genes on chromosome- helps in genetic mapping
Genetic mapping- knowing the location of various genes in our genome.
Used in HGP human genome project
SEX DETERMINATION
- Different organisms have different types of sex determination.
- Cytological observations in insects -- genetic or chromosomal basis of sex-determination.
- In 1891, Henking traced a specific nuclear structure all through spermatogenesis in few insects.
- He observed specific nuclear structure is located on 50 per cent of sperms only. The discovered X-body but was unable to explain its significance.
- Later- X body - X chromosome
- In insects,
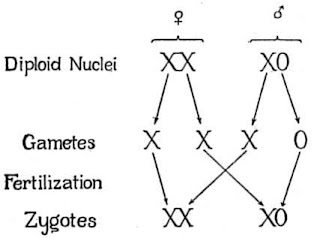
- XO type of sex determination is present.
- All the eggs have an additional X-chromosome besides the autosomes. Some sperms bear X-chromosome where as some do not.
- Eggs fertilized by sperm having having X-chromosome become females and those fertilized by sperms that do not have an X-chromosome becomes males.
- For example: grasshopper (males have only one X-chromosome besides autosomes and females have a pair of X-chromosomes)
Others- autosome
SEX DETERMINATION IN HUMANS
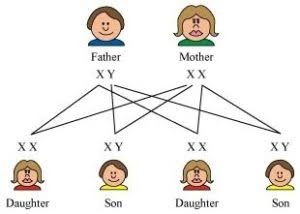
- XY type of sex determination
- Males (XY), Females (XX)
- Drosophila also has XY type of sex determination.
So till here, male forms 2 different gametes, so male- heterogametic
Female- homogametic
SEX DETERMINATION IN BIRDS
- ZW type of sex determination is seen in birds.
- Females have ZW and males have ZZ chromosomes.
- In birds sex is determined by type of ovum.
- In birds, females are heterogametic
SEX DETERMINATION IN HUMAN
SEX DETERMINATION IN BEES







No comments:
Post a Comment